Heard about Bitcoin?
That is what most people come across first. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin have become popular in discussions around financial technology.
However, Bitcoin runs on a certain technology, and there is more to that technology than just Bitcoin.
What then is Blockchain technology? What is it used for and who can use it?
Satoshi Nakamoto (a pseudonym), an unknown person/group behind the cryptocurrency Bitcoin conceptualized the first Blockchain which Bitcoin (the cryptocurrency) runs on way back in 2008.
Blockchain can be described as
1. A set of records or data that are time-stamped,
2. These sets of records cannot be tampered with,
3. They are neither controlled nor managed by a central entity. They are distributed across numerous digital (computer) entities.
Blockchain comprises two words: block (which represents blocks of data) and chain (depicting a cryptographic connection between these sets of data).
Cryptography (think of the word ‘crypt’) is a means of sending information through codes (that are hard to decipher or understand).
Blockchain technology is transparent. It’s a form of digital democracy. It is a distributed ledger shared among all participants and the data is accessible by everyone. The absence of a central point strengthens it against attacks or hacks.
What can Blockchain technology be used for?
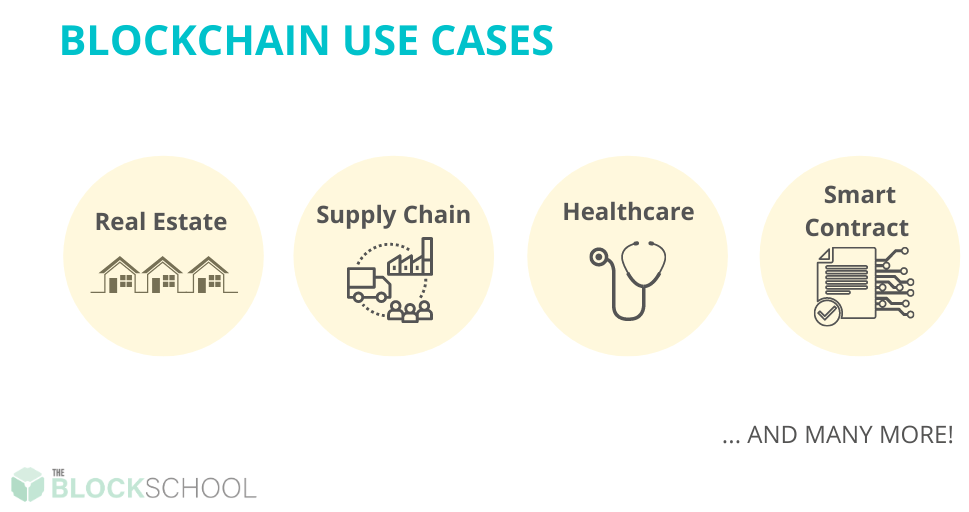
Blockchain technology can be deployed in numerous ways. A common use case includes record keeping, which blockchain technology’s flat and shared ledger can help to improve efficiency.
Use cases and sectors that can benefit include:
Real Estate: With its flat and shared ledger, Blockchain technology has the potential benefits of improving real estate record keeping.
Property records are time-consuming and hard to keep. Those who manage them are often boggled by heap after heap of record.
Blockchain technology can verify and store such data and eliminate cumbersome paperwork.
Case example: Lantmäteriet – Blockchain real estate system trialed by Swedish land registry. While the trial proved the possibility of such a system, much is needed such as regulatory approval before the system could be scaled up in the future.
Supply Chain: Supply chain is crucial to commerce, and blockchain technology has become increasingly essential to improving supply chain processes. Blockchain can help track the origin and sources of products, their movement, and ensure they get to the right destination. Blockchain technology is deployed extensively in the food supply chain.
Case example: Dimuto – Singapore-based company that enables fair and sustainable global trade of food products through a blockchain.DiMuto digitizes agrifood supply chains using blockchain technology and artificial intelligence.
Healthcare: Healthcare records often need to be private yet accessible when needed. Healthcare records can be safely encoded by healthcare providers to ensure that only the patient and trusted persons can access medical records through the patient’s private key.
Case example: Medicalchain – Health records on the blockchain. Enabling more transparent storing and sharing of health records
Smart Contracts: Blockchain technology can be used to create digital contracts that automatically executes agreements. Once the conditions set in the agreement are met, the contract self-executes.
Case example: Crowdsales via Ethereum blockchain – Projects running on Ethereum blockchain decentralized application (dApps) typically conduct an Initial Coin Offering (ICO) where participants can contribute BTC or ETH tokens for the project tokens, this swapping is usually facilitated by smart contract technology.
The utility of Blockchain technology are endless. In fact, more applications are emerging with the advancement and growing innovation in this sector.
Watch this space!
